In the first years of augmented reality’s emergence, the technology quickly garnered a reputation as an effective medium of entertainment with Pokemon Go, Snapchat filters, and video games. However, in 2024, augmented reality continues to evolve past these bold beginnings and is taking shape as an effective business tool.
Let’s delve into 12 augmented reality trends making moves in 2024 and explore each of them to see how they can benefit your business.
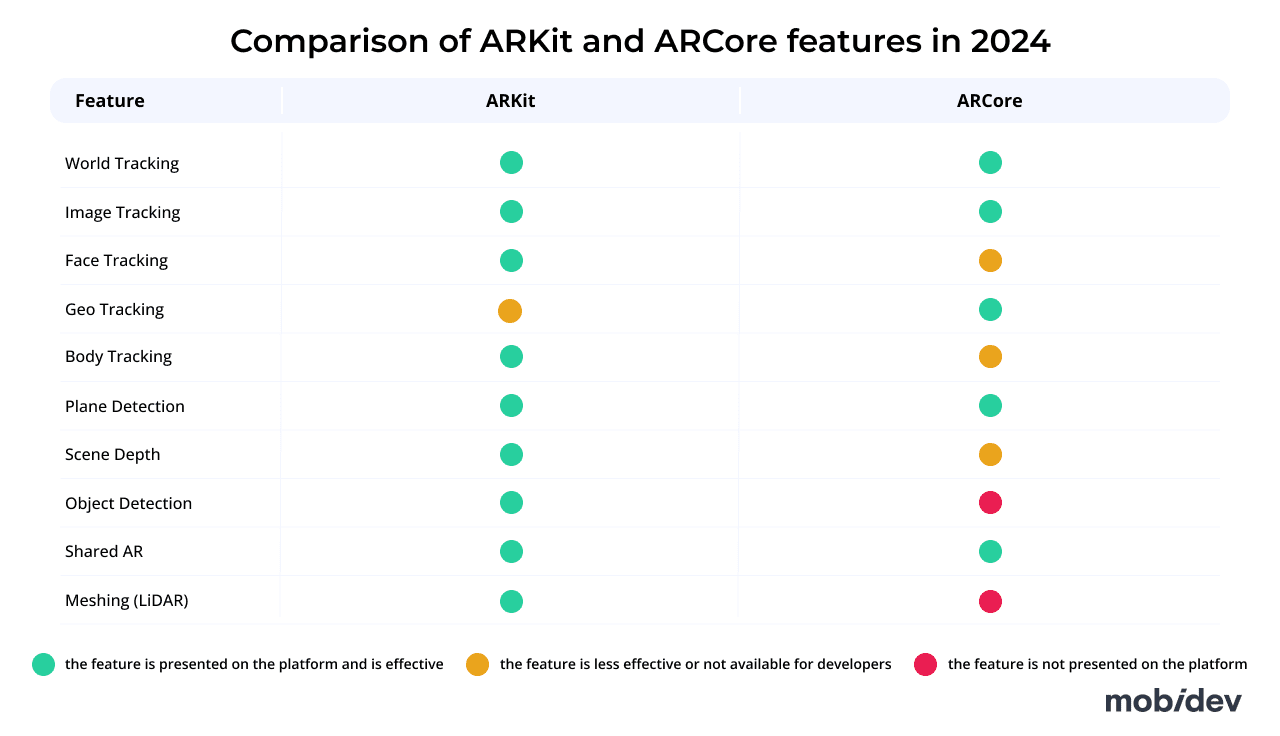
Trend #1 — Artificial Intelligence Powers the AR Future
Artificial intelligence development has always been closely tied to augmented reality. AI models are far more efficient at performing tasks like face and room scanning compared to human-written algorithms. However, in 2024, augmented reality technology is advancing beyond just using AI to interpret sensor data. There are a few important tasks that AI is achieving to supplement and enhance AR experiences:
- Constructing realistic human models and object scans: artificial intelligence has helped AR go from simply analyzing key points of a person’s face to actually reconstructing a face or other objects as a realistic, 3D model for use as an avatar or asset used in a virtual environment.
- Object detection and labeling: machine vision can identify objects and label them. This is useful for more than just identification, as virtual objects can be placed on top of ones in the real world to help facilitate AR interactions.
- Text recognition and translation: users can simply point their camera at some text and have it translated in real-time.
The recent explosion in generative AI models like Chat-GPT shows a great deal of promise for use in augmented reality’s future. For example, tools like Spline are already being used to create and manipulate 3D objects using natural language processing and generative AI. Textures and animations are also fair game.
AI is Assisting AR Device Setup and Troubleshooting
At MobiDev we experimented with combining AR and AI to solve today’s business challenges. For example, our engineers created a demo of a solution for onboarding and troubleshooting Wi-Fi routers. By using a smartphone camera, users can see directions to set up a Wi-Fi router and diagnose simple issues with 3D visual instructions and directions in augmented reality. The proof-of-concept application uses AR and AI to perform several troubleshooting and setup tasks, such as:
- Detecting the router itself
- Identifying whether cables need to be connected to the router
- Understanding the lights on the front of the router to determine the status of the device
Although AR remote assistance applications exist that can help accomplish this task, this case study achieves the same results without any human interaction aside from the user on-site.
Trend #2 — Leap into the Metaverse with AR Technologies
Although the initial hype of the metaverse quickly waned, the evolution of it and its surrounding technologies has persisted. During the metaverse’s hype cycle, a lot of attention was placed on decentralization, cryptocurrency, and blockchain. However, as interest in these topics declines, augmented reality appears to be the more durable and reliable technology that’s often associated with metaverse case studies. For instance, Apple’s Vision Pro headset is a testament to the potential on the horizon for AR technology.
Realistic Avatars: Bridging Real and Virtual Worlds
The future of social augmented reality is marked by a gradual transition away from cartoon-like avatars to more realistic-looking avatars. This enables more natural AR experiences. As an example, Apple demonstrated this technology in its announcements for the Apple Vision Pro.
They call these realistic avatars Spatial Personas which use machine learning to help display more body language and face tracking than ever before for social AR/VR interactions for FaceTime.
Apple isn’t alone. Meta is working on a similar concept called Codec Avatars. In fact, they have dedicated a deep generative model capable of creating these realistic 3D faces. By automating the process of creating a model in this way, realistic avatars will be far more feasible for use by consumers.
Trend #3 — Mobile Augmented Reality: From Games to Business Tools
Augmented reality technologies on mobile devices began as a fun toy. However, they have since evolved to become an incredibly useful tool for accomplishing a number of critical tasks like navigation and scene analysis. Businesses are using mobile AR more than ever, especially for tasks like remote assistance, training, product visualization, and more.
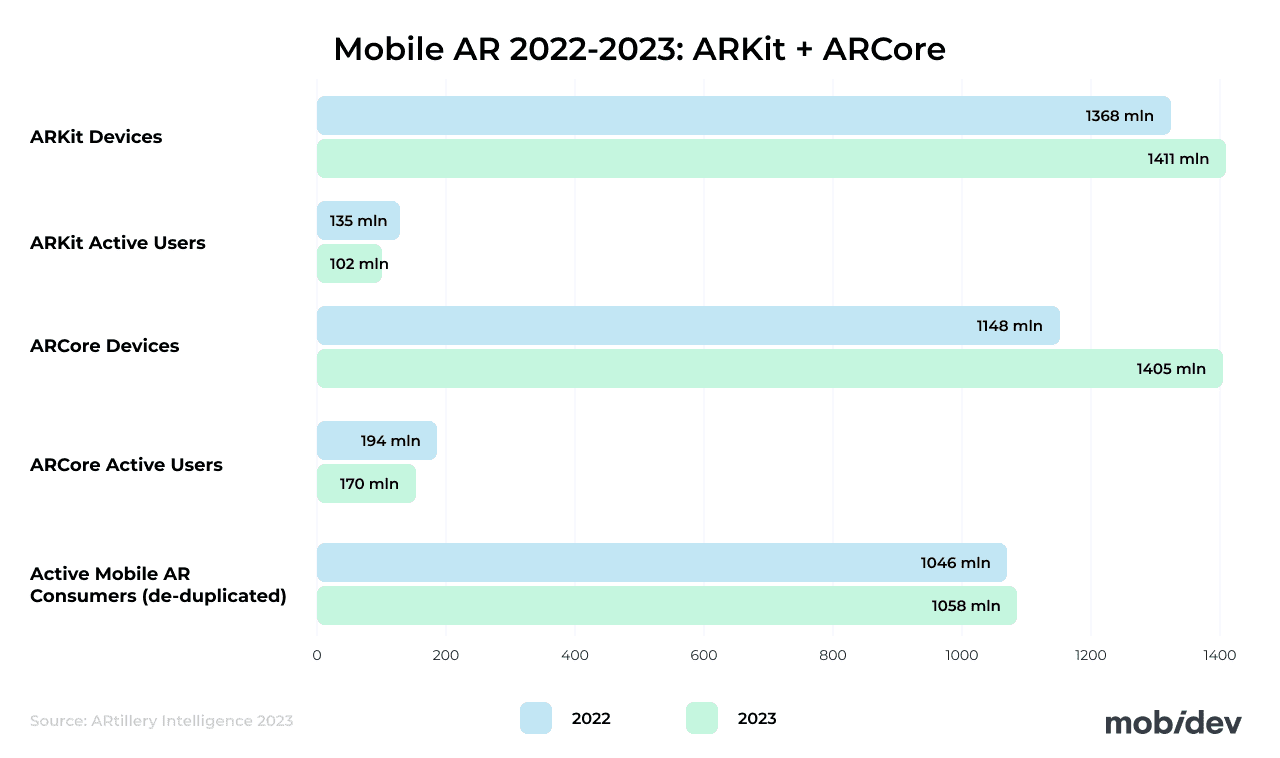
ARCore’s Latest Android AR Features
Google is evolving its Android augmented reality technology, ARCore, this year. The framework continues to build on the geospatial API presented in 2022, introducing Streetscape Geometry. This feature enables access to the geometry of buildings and terrain within a 100-meter radius. As a result, developers can build experiences that interact with the buildings and terrain in AR applications.
Rooftop anchors are another important feature that enables a digital object to be anchored to a rooftop. It uses the actual height and geometry of the building as a reference.
Another new function is geospatial depth. Also powered by streetscape geometry data, geospatial depth combines the streetscape data with the onboard depth sensor of a user’s smartphone to generate a 65-meter depth map.
Interestingly, Google has made scene semantics API available on iOS devices. With select features of ARCore available on iOS, Google boasts that the framework is now the world’s largest cross-device augmented reality platform.
Tech Consulting Services
Get expert help in choosing the right AR solution that best fits your business needs.
Contact usARKit 6: The Cutting Edge of AR on iOS Devices
Apple’s augmented reality framework continues to evolve to compete with Google’s ARCore. Some of the latest features are,
- 4K video recording during ARKit sessions
- LiDAR scanner depth API
- Instant AR powered by the LiDAR sensor’s plane detection
- Motion and pose capture
- Location anchors for new locations like Montreal, Sydney, Singapore, and Tokyo
One of the most powerful features that received enhancements in ARKit 6 is RoomPlan, which leverages the powerful LiDAR scanner on select devices to quickly create floor plans of structures with an iPhone or iPad. It also forms the foundation of powerful AR measurement tools.
Case Study:
AR Solution for Home RenovationARCore vs ARKit
Generally, the differences between ARCore and ARKit are less about software and more about hardware. Although Android devices exist that rival the advanced capabilities of newer LiDAR-capable iPhones, they are a select minority. Android devices are so diverse in their hardware configurations that it becomes much more difficult to build consistent experiences for them.
However, the same can technically be said for Apple’s devices. Not all iPhones have LiDAR scanners. Typically, the scanner is reserved for the Pro lineup of iPhones, as well as select iPad Pros. Without this advanced depth sensor devices won’t have as high-fidelity AR experiences.
Trend #4 – WebAR: Building Accessible Experiences
When we examined mobile AR’s growth in the last trend, one of the biggest challenges with mobile AR is hardware compatibility. The most powerful AR experiences, although useful and impressive, are always going to be out of reach for the vast majority of devices. WebAR on the other hand is a different approach, where simpler AR experiences are provided through a web browser compatible with most devices with a camera.
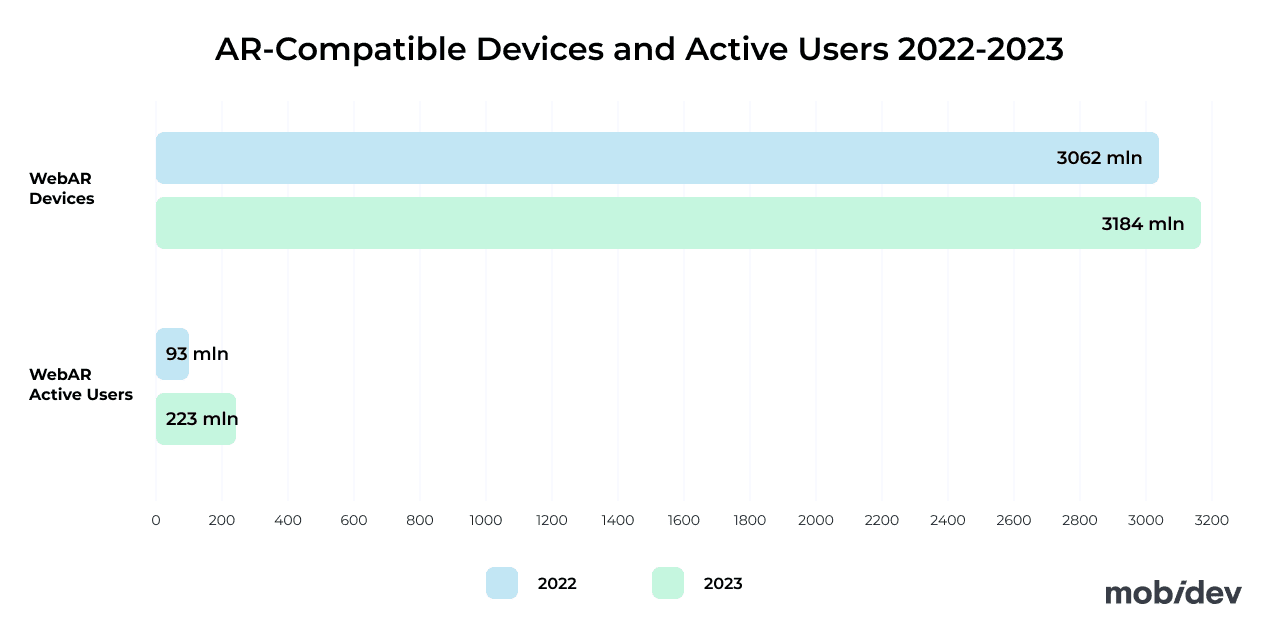
Although WebAR solutions are less powerful than native mobile AR applications, the accessibility provided is WebAR’s greatest strength. The ability to provide face filters, changing color of hair or objects, background replacement, and simple 3D objects on just about any device regardless of hardware is extremely useful.
The future of augmented reality on the web is closely tied to AI. One of the most popular WebAR development platforms, 8th Wall from Niantic, has introduced a number of new features available to developers to build immersive applications on the web. Web-based applications can now replace the sky with images and textures. These images and textures can even be generated using AI models like DALL-E and Stable Diffusion. Shared AR experiences are also possible with others.
Trend #5 – Cross-Platform Augmented Reality Applications
The ultimate goal of many companies producing augmented reality experiences is to target as many of their customers as possible. However, several challenges immediately arise:
- Different platforms have different limitations and capabilities, and audiences may have a variety of devices at their disposal.
- Building AR experiences for each platform natively can be expensive and requires dedicated teams to ensure consistency between each platform.
- Cross platform development tools for augmented reality cannot achieve the same level of power and quality as native applications.
Cross-platform applications are best for apps that aren’t that complicated. However, if your app needs more power and better-quality features, building the app natively is the best option.
For example, if you are creating an online store where 90% of the functionality is not platform-dependent, that does not require maximum performance and has a simple product preview module in AR, then you can opt for cross-platform AR. But if we deal with an application whose functionality requires maximum performance or is platform-dependent, then the native option is better. This applies to projects such as 3D scanning or AR navigation.
Trend #6: Wearable Augmented Reality Experiences Are Here
The past few years have seen major changes in the wearable augmented reality industry. Apple has finally brought the Apple Vision Pro to market. Although extremely premium in price, it marks a significant milestone in the road to the future of augmented reality headsets for consumers.
One of the main themes of wearable augmented reality experiences is you can generate a screen and use apps from your computer anywhere you want. Alternatively, you can watch a movie on a giant screen from anywhere in the house. As augmented reality headsets take us into a new era of interfaces, spatial computing is necessary for us to naturally interact with those machines.
Meanwhile, Meta has launched the Quest 3 and Quest Pro with full color pass-through features, meaning that they both have very affordable augmented reality capabilities. One of the mixed reality features that Meta has promoted for Meta Quest 3 is PianoVision, an app that helps users learn to play piano using either Synesthesia-style 3D notes, or with sheet music. Labeled keys can help beginners as well.
Augmented Reality and Apple Vision Pro
As mentioned previously, Apple’s Vision Pro is a highly promising advancement in the AR/VR market. Boasting cutting-edge attributes like high-resolution displays, an extensive range of sensors, built-in spatial sound, as well as eye and gesture tracking functionalities, it looks like a highly functional business solution.
For instance, within the retail industry, businesses can leverage its capabilities to present products within immersive 3D environments. This empowers customers to virtually engage with products before making a purchase decision.
The development process for Apple’s Vision Pro revolves around the visionOS SDK. Developers can utilize familiar Apple tools, such as SwiftUI, RealityKit, ARKit and more, to build apps for this platform. It’s also possible to adapt existing applications for Vision Pro using the visionOS SDK. The adjustment efforts required will vary based on the specific application. While a significant portion of the current code can be transferred and reused, some adjustments and testing will still be necessary.
Combining ARKit and VisionOS allows for advanced functionalities like skeletal hand tracking and accessibility features. This way, users can interact with the virtual experience with gestures (eye movements, voice commands, head movements, and hand gestures). Developers with ARKit and iOS development experience can easily extend their app development skills to Apple Vision Pro.
So, the future of augmented reality on affordable mixed reality headsets is still developing, but progress is being made.
Trend #7 – Augmented Reality in Marketing
There are a number of different applications for Augmented Reality in the marketing industry. Augmented reality business cards, user manuals, and product demonstrations are fairly simple to transform into immersive experiences. This is a great way to stand out against the competition. Using ARKit, our developers at MobiDev created a demonstration of AR business cards.
In another example, we created an AR user guide for a coffee machine. This helps users better understand how to operate the device. Such manuals can be created for different products and services.
Augmented reality technology in marketing continues to make businesses more money. AR Insider reports that global augmented reality’s future revenue is expected to climb as high as $39.8 billion in 2027.
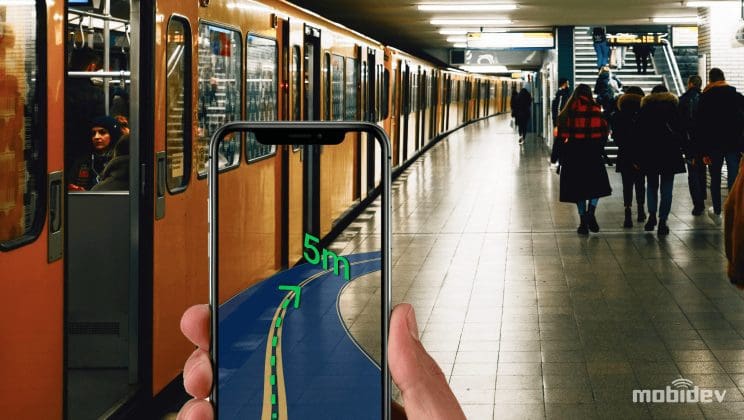
Trend #8 – Indoor and Outdoor Navigation with AR
For years, innovators have sought to create immersive navigation experiences for indoor and outdoor environments. Augmented reality has significant promise as an interface for these technologies because of its immersion. Instead of glancing down at a screen for contextual directions on a map, 3D markers and guides within a user’s vision or through a viewfinder keep the user in the moment and more aware of their surroundings. The future of augmented reality navigation does come with nuance, as no one method or technique excels in all locations.
Indoor Navigation Powered by Augmented Reality
Indoor navigation is still largely limited by its own positioning constraints. It’s possible to create AR indoor navigation systems, but it will not be as accurate as we would like. For example, indoor navigation will not be able to lead the customer to a specific product on the store shelf, but it can indicate the direction to the correct department where the customer can find this product.
There are typically three popular approaches to indoor navigation:
- Beacons: Bluetooth LE, Wi-Fi RTT, or UWB
- Markers: Visual markers identified by a device with an AR framework
- VPS (Visual Positioning System)
Our engineers at MobiDev demonstrated marker-based AR indoor navigation for use at a corporate campus using ARKit with success. Marker-based AR indoor navigation is cheaper to implement than beacons but may be subject to some problems like obstruction of markers or misconfiguration.
Outdoor Augmented Reality Navigation
When it comes to positioning, outdoor navigation has a clear advantage in most situations. GPS can provide almost perfect positioning for devices in most environments. However, there are two major issues to consider:
- Rural areas with great access to GPS aren’t necessarily where augmented reality navigation is in demand, as these areas may be very flat and have long distances between places the user needs to make turns. If the user is driving, regulations may prevent them from using heads-up displays for AR directions.
- Urban areas with dense skyscrapers may inhibit GPS signals. Although demand for AR navigation is higher in these areas, positioning may be less accurate.
Google and Apple have implemented VPS (Visual Positioning Systems) in their AR platforms that compare databases of street view images to locate a user’s position before generating AR directions in a scene. However, if the location is unknown or weather conditions aren’t clear, such as during heavy fog, these visual systems may not operate as expected.
However, during good weather conditions, app developers can use each platform’s various tools to anchor 3D objects to geographic coordinates and structures, allowing for more immersive experiences when navigating or exploring certain areas.
Trend #9 – Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Just as in the previous navigation examples, augmented reality excels in providing interfaces to users at the moment, hands-free. Wearable displays like Microsoft’s HoloLens are already being used by doctors to assist with surgery by providing doctors with important information like patient vitals while staying focused on the task at hand. Although the future of HoloLens is uncertain, devices like the Apple Vision Pro are competitively priced against it. This indicates that even if Microsoft isn’t able to maintain a foothold on the market, other players will enter to meet the demand.
Combined with machine learning algorithms, AR technology can become an efficient option for disease detection. Google is continuing to update their AR microscope repository on GitHub, allowing developers and healthcare professionals to use augmented reality to better detect cancerous cells. It’s clear that the future augmented reality will continue to improve the efforts of not only medical professional productivity, but also the advancement of medical science.
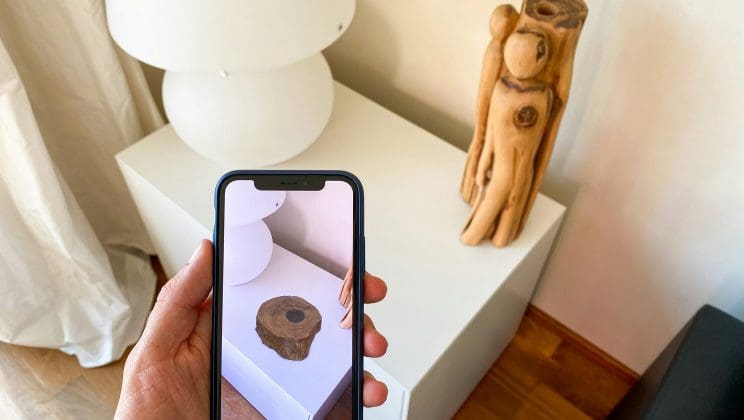
Trend #10 – Retail and Augmented Reality Shopping
Virtual try-on solutions continue to be a major driver of AR’s use in retail applications. Businesses are improving the ways that their customers shop online, and immersive experiences play a major role in that mission. Being able to see furniture and other objects in augmented reality to see how they would really look in a room is a popular feature used by stores like IKEA, Target, and more.
Virtual fitting room technology also continues to improve. Body measurement techniques have gotten more advanced, allowing customers to better personalize their experience when shopping for clothes online.
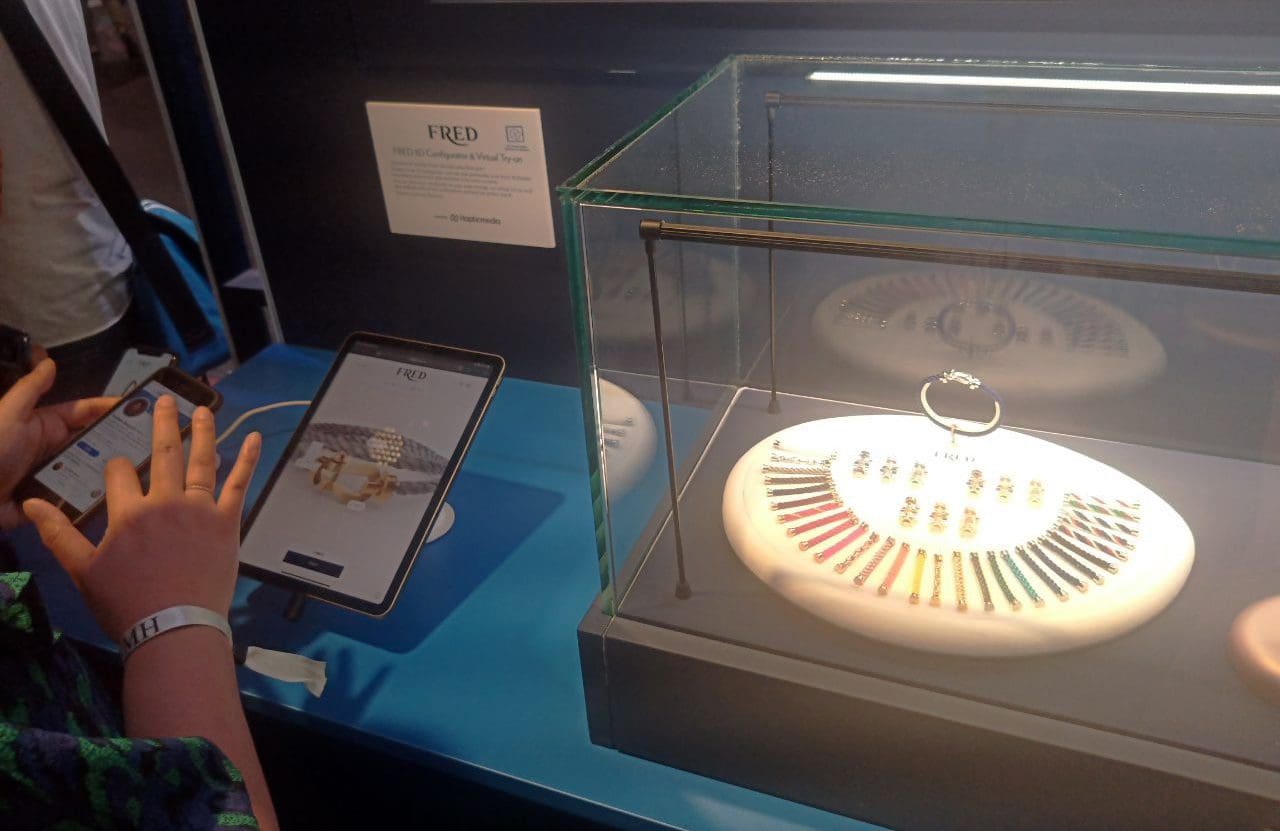

FRED Jewelry Virtual Try-On Presented on Viva Tech 2022
One unique example of the future of augmented reality virtual try applications is a recent partnership between e.l.f. Cosmetics and Google through interactive YouTube advertisements. During a video ad for makeup, users can click on the ad to start up an AR experience where they can see how the cosmetics look on their faces.
Trend #11 – Augmented Reality in Manufacturing
The future of augmented reality also has significant benefits for manufacturing applications. For example, AR is making strides in assisting in areas such as:
- Worker training: digital twins and simulated experiences can help workers understand and respond to serious situations in an immersive environment
- Routine maintenance: AR can highlight elements of machines that need to be serviced to make maintenance easier for technicians
Another major use case is AR remote assistance. To add further depth to remote assistance video calls, off-site engineers leverage AR to highlight and point to elements in 3D space to help end users solve problems without dispatching a field technician.
Trend #12 – Augmented Reality in the Automotive Industry
Even the automotive industry is benefiting from innovations in augmented reality. Some of these innovations are:
- Car sales: AR as a marketing tool
- Remote assistance: providing guided assistance and diagnostics for drivers
- Parking spot detection: highlighting empty parking spots in busy garages
- Detecting driver drowsiness: using facial recognition to detect reduced attentiveness and helping drivers wake up or regain focus
- Heads-up display (HUD) for drivers: assisting drivers by putting directions and highlighting dangers within their field of vision
Heads Up Displays
Providing drivers with heads-up display information is something we may find available soon. Mercedes Benz is working on a car for release in 2024 with an AR heads up display without a headset. Most attempts to build AR HUD features for cars have involved a headset.
However, given that safety is a priority for drivers, there is still room for improvement. As the future of augmented reality progresses, manufacturers can find a way to make AR experiences more accessible to drivers. Without having to make them wear a headset, drivers would be not only more comfortable but more protected from failure in case the headset somehow fails, causing them to lose their vision entirely.
Waking Up Drowsy Drivers
The WakeUp app developed by MobiDev is another great example of using augmented reality in the automotive industry. The objective of WakeUp is to help keep drivers awake by using ARKit facial recognition technology to detect when a driver’s eyes are closed or their head is tilted. If the eyes remain closed or the head is tilted for too long, the device plays an alarm to help wake the driver up.
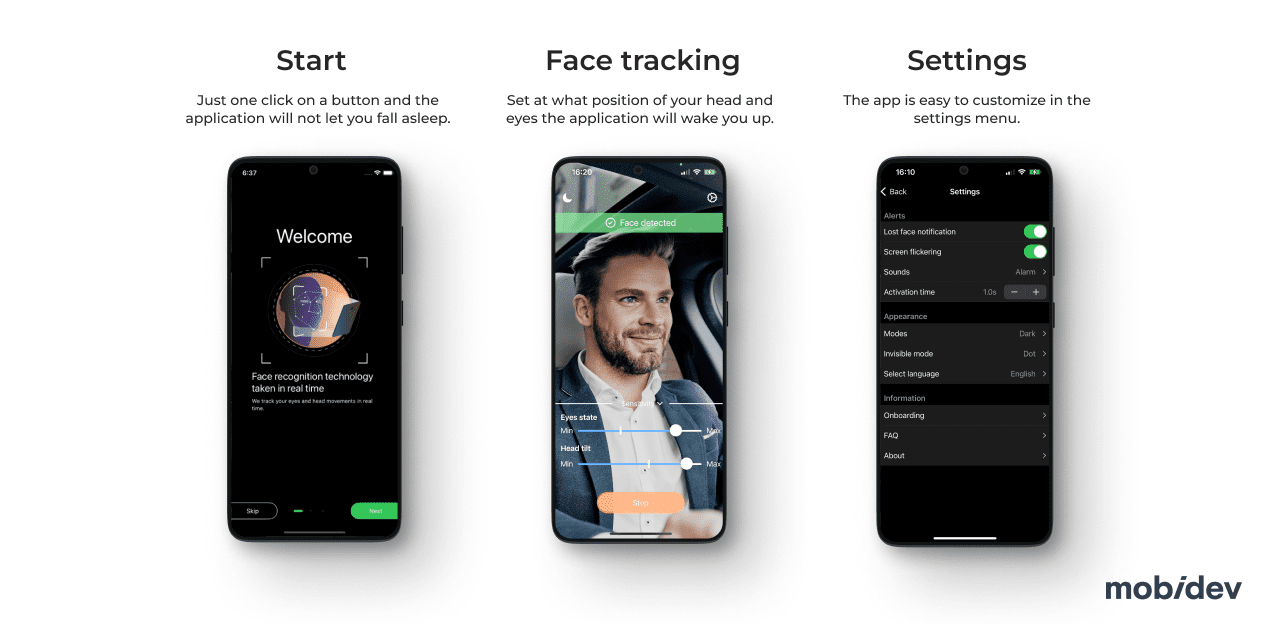
WakeUp App by MobiDev
There is room for this technology to grow. For example, a TrueDepth camera with its infrared sensing can help to perform head and eye tracking in complete darkness. Also, artificial intelligence could detect behaviors from a driver that indicate that they might become drowsy and alert the driver before it’s too late. We plan to continue moving in this direction for our projects in the future.
The Future of Augmented Reality Technology
In 2020, the total value of AR and VR technologies was estimated at $15.3 billion and is expected to grow to $198 billion by 2025 (Statista). According to the ISACA report, 70% of consumers believe that AR can provide them with benefits, and businesses are ready to meet these needs and contribute to the development of the augmented reality market.
It is becoming increasingly clear that the future of augmented reality in all sectors will have close ties with artificial intelligence. AI’s rise to prevalence and initial hype seem to still be running strong for now. However, its potential to advance augmented reality experiences will likely persist even after interest in AI begins to decline and stabilize. This is especially the case considering that augmented reality has proven itself as a valuable business tool, not just a medium for gaming or entertainment.
Working with experienced augmented reality developers can help you achieve your vision of success. If you’re ready to take that first step into the future and realize your potential, contact us today so we can talk about how we can meet your needs.




